- Home
- Symmetry Blog
- Defining Immersive Technologies
Defining Immersive Technologies
What You Need to Know
About Jari Haiston
By this time into 2024, most of us know that immersive technologies transport users into mesmerizing virtual realms, blurring the lines between fiction and reality without the constraints of physical existence. Also known as extended reality (XR), immersive tech encompasses augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR), and virtual reality (VR) experiences. Harnessing the full potential of XR demands robust computing, and Symmetry Electronics empowers developers to design requires powerful computing to operate, and Symmetry Electronics has everything developers need to design state-of-the-art XR devices.
What is Virtual Reality?
In a VR experience, users can see, hear, and interact with virtual technology. Although physical touch remains beyond reach, VR generates a profound sensation of actually inhabiting a digital space. There are four main types of VR technology:
Fully Immersive Virtual Reality
Fully immersive VR is the most encompassing virtual experience, where users are made to feel like they have physically been transported to a digital environment. The immersive journey is facilitated by sensors embedded in body connectors, helmets/headsets, and gloves that enable users to interact with the virtual environment around them through physical movements. Picture yourself navigating a gaming landscape, where every motion of your body translates into actions in the gaming world.
Non-Immersive Virtual Reality
In contrast to its fully immersive counterpart, non-immersive VR doesn’t directly engages with users on a sensory level. While users can manipulate characters or activities within the virtual environment, they don’t become the focal point of the digital space. Many gaming consoles offer non-immersive experiences, providing users with control over gameplay elements without completely entering a virtual world.
Semi-Immersive Virtual Reality
As the name suggests, semi-immersive VR strikes a balance between fully immersive and non-immersive experiences. Users find themselves navigating a 3D space or environment, able to move around the virtual realm using VR equipment such as headsets or computers, albeit without physical exertion. This versatile form of VR has applications in various domains, from offering realistic virtual tours of real estate properties and hotels to facilitating immersive educational experiences in schools.
Collaborative Virtual Reality
Imagine a shared digital space where users from separate locations converge, interacting with one another in real-time though avatars or 3D representations. This collaborative VR experience transcends physical barriers, fostering communication and collaboration among individuals through chat interfaces, headsets, and microphones. Whether it’s conducting virtual meetings or exploring virtual environments together, collaborative VR redefines the concept of shared spaces in the digital age.
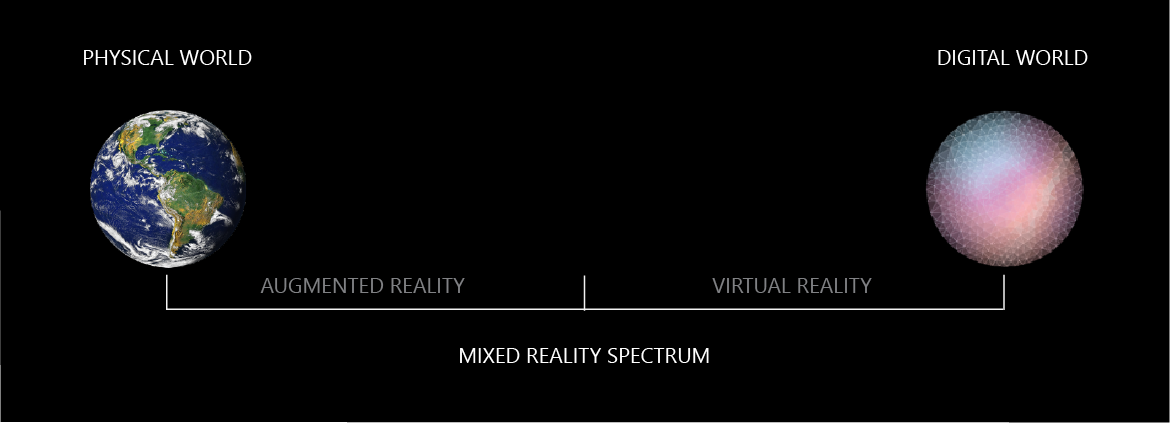
Figure 1: Mixed Reality Spectrum
Source: Microsoft
What is Augmented Reality?
Often debated as its own unique type of technology in the VR community, augmented reality differs from other types of VR (Figure 1) in that it interacts with real-world environments. Augmented reality is capable of viewing the space around a user to project a virtual entity into it. While the entity is not physically present, users can interact with it through the device that is projecting the entity.
Marker Based Augmented Reality
Marker-based AR requires a visual marker, like a QR code, to operate. Apps like Snapchat use this type of AR to help users add to their contacts.
Markerless Augmented Reality
Markerless AR utilizes GPS, digital compasses, velocity meters, and accelerometers to operate. Apps like Google Maps run off of this type of AR.
Projection Based Augmented Reality
Projection-based AR utilizes artificial light to operate. Light can be in the form of lasers, mirrors, or cameras to create a projection with which users can interact.
What is Mixed Reality?
While mixed reality (MR) sounds similar to AR, MR allows users to blend real and virtual elements. In comparison to AR and VR (Figure 2), MR allows users to further integrate elements of the real-world and virtual space. In an MR experience, users can react with 3D entities the same way they would in the real-world. As the newest form of immersive technology, companies are working to adopt MR experiences. It’s thought that MR technology can modernize design, modeling, and prototyping in a virtual environment.
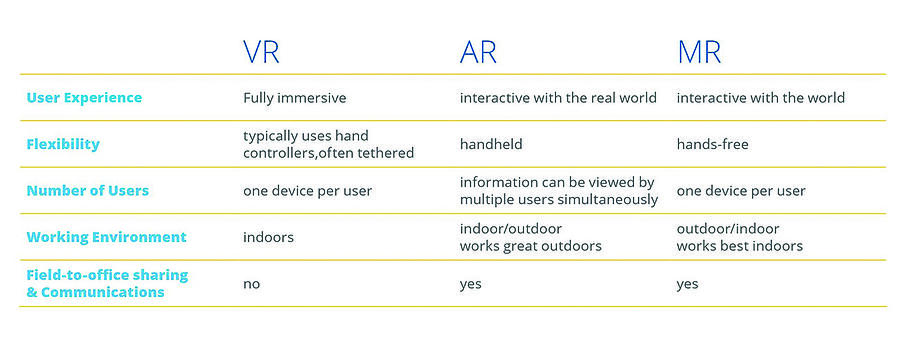
Figure 2: Comparison of virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality.
Source: Trimble SiteVision
The Future of Immersive Technologies:
The future of immersive technologies is bright. Marketwatch reported that “The Global Immersive Technologies Market is expected to grow at a significant CAGR of 38% by 2028.” Besides gaming and decorating, extended realities can serve to benefit companies and societies in altruistic ways:
- Healthcare – XR experiences can enhance surgical simulations
- Virtual travel – XR technology can bring remote destinations to a user’s living room. Virtual travel will for more integration of culture, art, and understanding into society.
- Military and Defense – Like healthcare, XR technology in military and defense industries can help save lives by enhancing training simulations.
If you’re a developer looking to design the industry’s next immersive device, Symmetry Electronics has a wide range of solutions available to make your project a success. Our portfolio can empower your ideas into tangible realties that captivate and inspire. Check out our top recommendations that are sure to enrich your design and redefine possibilities in immersive tech.
Digi ConnectCore® 93 from Digi International is an embedded system-on-module SoM that features dual-band wi-fi 6 and Bluetooth 5.3 connectivity. ConnectCore 93 products are ideal solutions for IoT, automation, human-machine interface (HMI), equipment monitoring, audio/voice, edge computing, and machine learning (ML) applications.
The Tunsten700 SMARC (smart mobility structure) series from Laird Connectivity is powered by MediaTek’s state-of-the-art Genio 700 processor, is ideally suited for applications in high-end digital signage and graphics, AI applications, smart cameras, industrial tablets/handhelds, industrial IoT (IIoT)/vision systems, smart fitness equipment, autonomous robots, and retail POS.
MediaTek’s sophisticated Genio 1200 EVK is a edge-AI IoT platform that delivers a high-end solutions for applications spanning industrial, smart home, interactive retail, and commercial sectors. It’s a feature-rich evaluation kit with exceptional performance in edge processing, multimedia capabilities, and multitasking operating systems.
xcore®.ai solutions from XMOS deliver a wide range of cutting-edge features to enhance your VR device designs. With unmatched performance, flexibility and scalability, xcore.ai products are well suited for a broad variety of applications, including Edge AI, smart home, audio/visual, smart speakers, and much more.