- Home
- Braemac Blog
- Accelerometers vs Gyroscopes
Accelerometers vs Gyroscopes
About Symmetry Electronics
Established in 1998, Symmetry Electronics, a Division of Braemac, is a global distributor of electronic components and systems. Combining premier components and comprehensive value-added services with an expert in-house engineering team, Symmetry supports engineers in the design, development, and deployment of a broad range of connected technologies.
Exponential Technology Group Member
Acquired by Berkshire Hathaway company TTI, Inc. in 2017, Symmetry Electronics is a proud Exponential Technology Group (XTG) member. A collection of specialty semiconductor distributors and engineering design firms, XTG stands alongside industry leaders TTI Inc., Mouser Electronics, and Sager Electronics. Together, we provide a united global supply chain solution with the shared mission of simplifying engineering, offering affordable technologies, and assisting engineers in accelerating time to market. For more information about XTG, visit www.xponentialgroup.com.

Accelerometers and Linear Motion Explained

Types of Accelerometers
- 1-axis: Detect motion along a single direction.
- 2-axis: Measures motion along two directions.
- 3-axis: Tracks motion in three-dimensional space, giving a complete picture of linear motion and linear acceleration.
Utilizing Gyroscopes for Rotational Motion

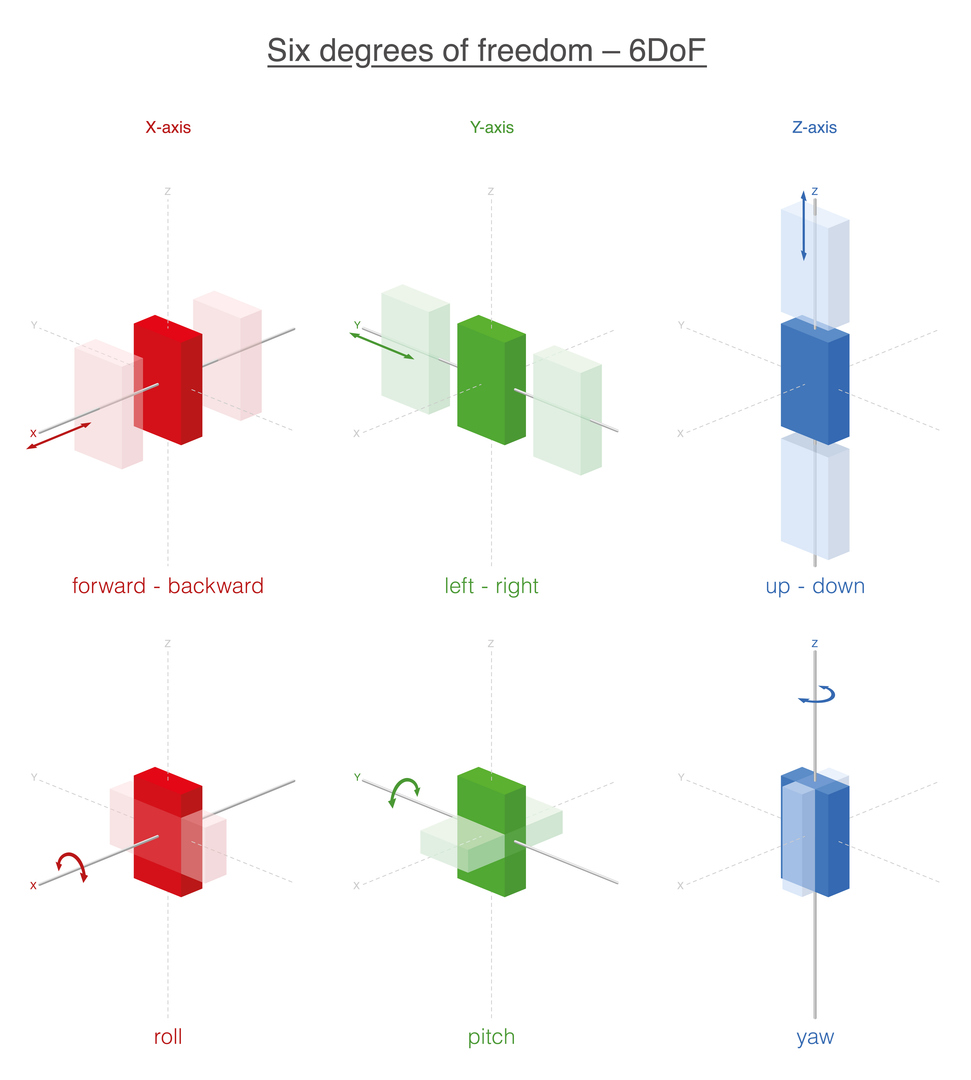
Combining Accelerometers and Gyroscopes: 6 Degrees of Freedom (6 DoF)
Motion Sensor Solutions for Real-World Designs
| Sensor Type | Key Differences | Primary Use Case | Common Applications |
| Accelerometer only | Linear motion only; no true rotation tracking | Straight-line movement and basic orientation | Step counters, tilt detection in smartphones, basic robotics |
| Gyroscope only | Measures rotation; may drift over time | Rotational motion and rapid orientation changes | Drones, gaming controllers, aircraft navigation, image stabilization |
| Accelerometer + Gyroscope | Linear + rotational data; 6-DoF | Full 3D motion and precise orientation tracking | VR/AR, autonomous systems, advanced robotics |
Motion Sensor Solutions Now Available at Braemac Americas
Motion sensors are devices that detect movement, orientation, or position, and they are widely used in modern applications such as IoT devices, robotics, consumer electronics, and industrial systems. Accelerometers and gyroscopes enable real-time motion detection and orientation tracking across many sensor applications.
The difference between an accelerometer and a gyroscope is the type of motion each sensor measures. An accelerometer measures linear motion and linear acceleration, while a gyroscope measures rotational motion or angular movement around an axis.
You should use a 3-axis motion sensor when motion needs to be tracked in three-dimensional space. A 3-axis accelerometer measures linear motion along three axes, while a 3-axis gyroscope tracks rotational motion, enabling accurate orientation tracking.
6 Degrees of Freedom (6 DoF) in motion sensing refers to tracking movement along three linear axes and rotation around three axes. This is achieved by combining a 3-axis accelerometer with a 3-axis gyroscope to provide a complete picture of position and orientation.
Accelerometers and gyroscopes are often combined in IoT sensors to improve accuracy for real-time motion detection and orientation tracking. Accelerometers handle linear motion, while gyroscopes provide precise rotational data, reducing errors in sensor applications.
Choosing the right motion sensor depends on the type of movement and level of precision your application requires. Accelerometers are typically used for linear motion, gyroscopes for rotational motion, and combined 3-axis sensors provide full 6 DoF tracking for advanced IoT and robotics applications. Braemac Americas can help engineers evaluate these options and select the right sensors for their specific design needs.




